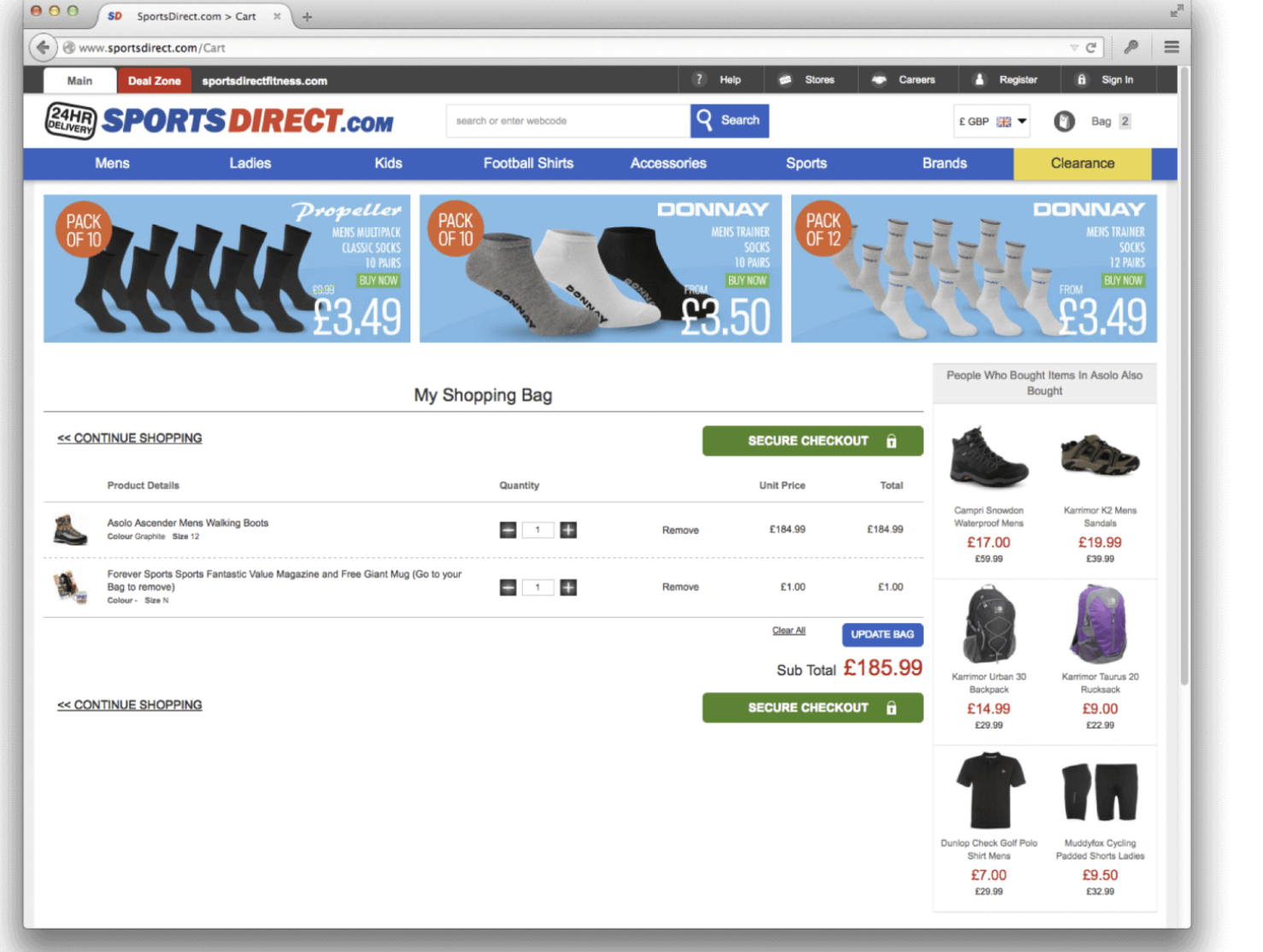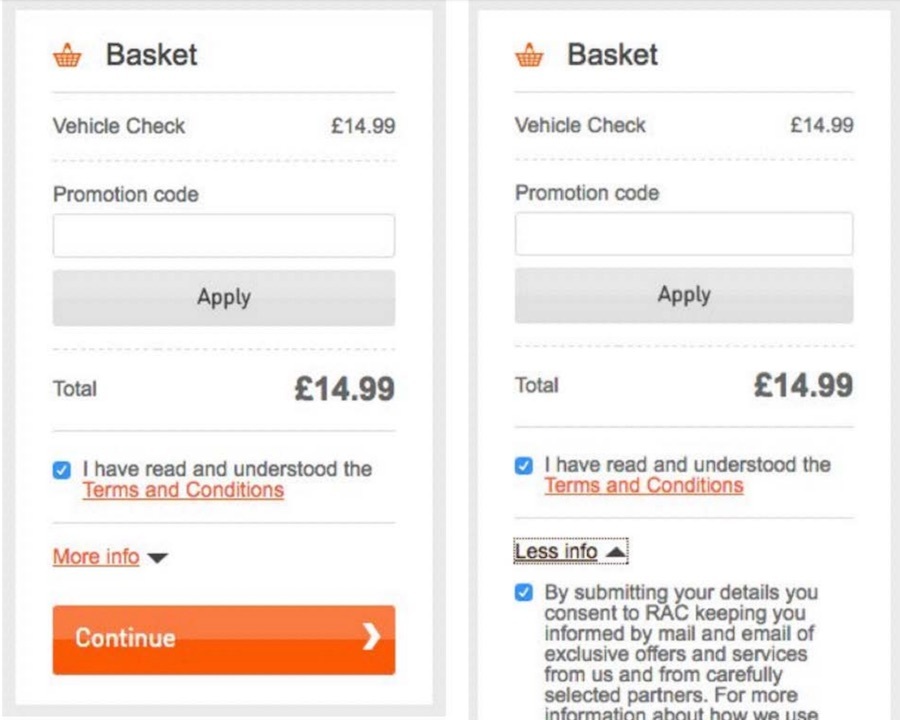
The example you've just experienced is called Sneaking.
- Sneaking occurs when websites intentionally hide or obscure important information from users, such as additional costs or unwanted consequences. This tactic is often used to manipulate users into taking actions they wouldn't normally choose.
- In the previous example, if you overlook the Sneaking tactic, you might find that these websites add extra items to your order without your consent. Now, you're left with additional items you never wanted in the first place, and it's up to you to remove them.
1. You can double-check everything before making the final decision.
2. You can leave or report the websites that use Sneaking.